Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
06. Parameter tests#
The modeller emg3d has quite a few parameters which can influence the speed
of a computation. It can be difficult to estimate which is the best setting. In
the case that speed is of utmost importance, and a lot of similar models are
going to be computed (e.g. for inversions), it might be worth to do some
input parameter testing.
IMPORTANT: None of the conclusions you can draw from these figures are applicable to other models. What is faster depends on your input. Influence has particularly the degree of anisotropy and of grid stretching. These are simply examples that you can adjust for your problem at hand.
import emg3d
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import LogNorm
plt.style.use('bmh')
def plotit(infos, labels):
"""Simple plotting routine for the tests."""
plt.figure()
# Loop over infos.
for i, info in enumerate(infos):
plt.plot(info['runtime_at_cycle'],
info['error_at_cycle']/info1['ref_error'],
'.-', label=labels[i])
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel('Time (s)')
plt.ylabel('Rel. Error $(-)$')
plt.yscale('log')
# Survey
zwater = 1000 # Water depth.
src = [0, 0, 50-zwater, 0, 0] # Source at origin, 50 m above seafloor.
freq = 1.0 # Frequency (Hz).
# Mesh
grid = emg3d.construct_mesh(
frequency=freq,
min_width_limits=100,
properties=[0.3, 1., 1., 0.3],
center=(src[0], src[1], -1000),
domain=([-1000, 5000], [-500, 500], [-2500, 0]),
center_on_edge=False,
)
print(grid)
# Source-field
sfield = emg3d.get_source_field(grid, source=src, frequency=freq)
# Create a simple marine model for the tests.
# Layered_background
res_x = 1e8*np.ones(grid.shape_cells) # Air
res_x[:, :, grid.cell_centers_z <= 0] = 0.3 # Water
res_x[:, :, grid.cell_centers_z <= -1000] = 1. # Background
# Target
xt = np.nonzero((grid.cell_centers_x >= -500) &
(grid.cell_centers_x <= 5000))[0]
yt = np.nonzero((grid.cell_centers_y >= -1000) &
(grid.cell_centers_y <= 1000))[0]
zt = np.nonzero((grid.cell_centers_z >= -2100) &
(grid.cell_centers_z <= -1800))[0]
res_x[xt[0]:xt[-1]+1, yt[0]:yt[-1]+1, zt[0]:zt[-1]+1] = 100
# Create a model instance
model_iso = emg3d.Model(grid, property_x=res_x, mapping='Resistivity')
# Plot it for QC
grid.plot_3d_slicer(model_iso.property_x.ravel('F'),
pcolor_opts={'norm': LogNorm()})
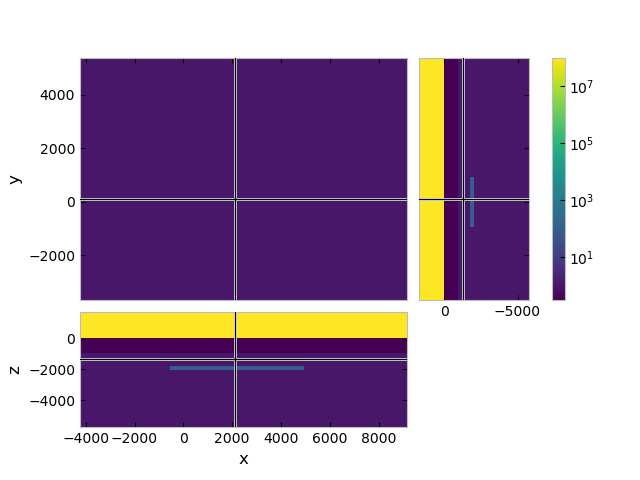
TensorMesh: 76,800 cells
MESH EXTENT CELL WIDTH FACTOR
dir nC min max min max max
--- --- --------------------------- ------------------ ------
x 80 -4,233.88 9,146.56 100.00 912.68 1.25
y 24 -3,667.19 5,375.78 100.00 1,708.59 1.50
z 40 -5,764.95 1,752.46 100.00 857.19 1.31
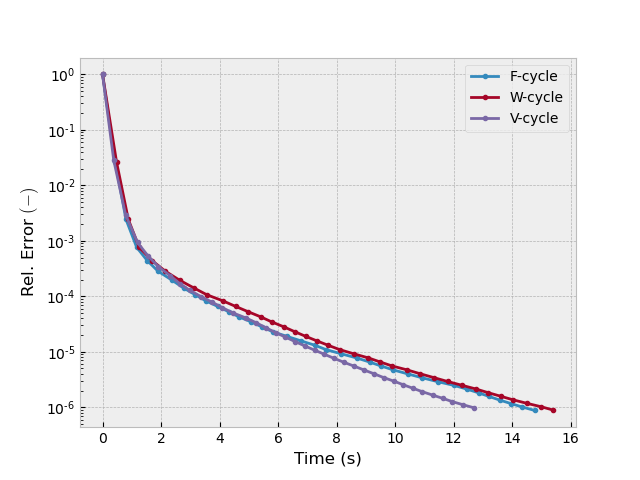
Test 1: F, W, and V MG cycles#
inp = {'model': model_iso, 'sfield': sfield, 'return_info': True,
'sslsolver': False, 'semicoarsening': False, 'linerelaxation': False}
_, info1 = emg3d.solve(cycle='F', **inp)
_, info2 = emg3d.solve(cycle='W', **inp)
_, info3 = emg3d.solve(cycle='V', **inp)
plotit([info1, info2, info3], ['F-cycle', 'W-cycle', 'V-cycle'])
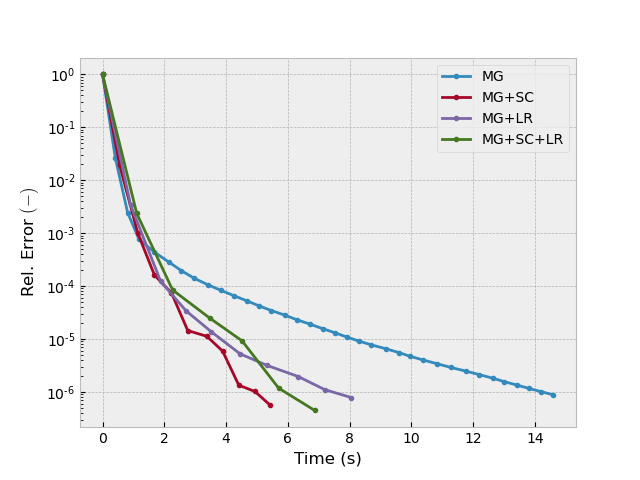
Test 2: semicoarsening, line-relaxation#
inp = {'model': model_iso, 'sfield': sfield, 'return_info': True,
'sslsolver': False}
_, info1 = emg3d.solve(semicoarsening=False, linerelaxation=False, **inp)
_, info2 = emg3d.solve(semicoarsening=True, linerelaxation=False, **inp)
_, info3 = emg3d.solve(semicoarsening=False, linerelaxation=True, **inp)
_, info4 = emg3d.solve(semicoarsening=True, linerelaxation=True, **inp)
plotit([info1, info2, info3, info4], ['MG', 'MG+SC', 'MG+LR', 'MG+SC+LR'])
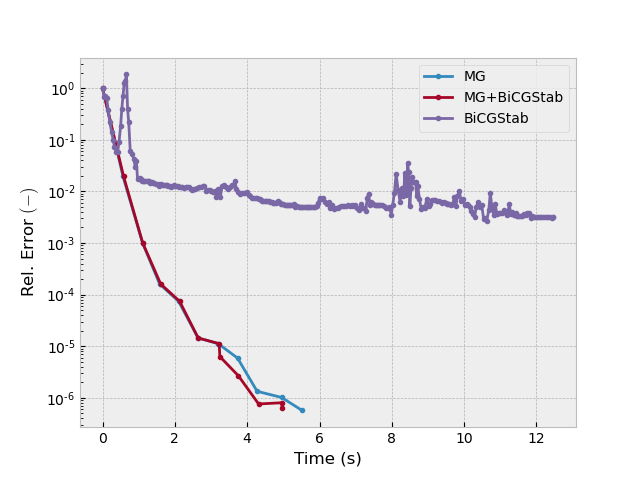
Test 3: MG and BiCGstab#
inp = {'model': model_iso, 'sfield': sfield, 'return_info': True, 'maxit': 500,
'semicoarsening': True, 'linerelaxation': False}
_, info1 = emg3d.solve(cycle='F', sslsolver=False, **inp)
_, info2 = emg3d.solve(cycle='F', sslsolver=True, **inp)
_, info3 = emg3d.solve(cycle=None, sslsolver=True, **inp)
plotit([info1, info2, info3], ['MG', 'MG+BiCGStab', 'BiCGStab'])
* WARNING :: Error in bicgstab (-10)
Test 4: nu_init, nu_pre, nu_coarse, nu_post#
inp = {'model': model_iso, 'sfield': sfield, 'return_info': True,
'sslsolver': False, 'semicoarsening': True, 'linerelaxation': False}
_, info1 = emg3d.solve(**inp)
_, info2 = emg3d.solve(nu_pre=0, **inp)
_, info3 = emg3d.solve(nu_post=0, **inp)
_, info4 = emg3d.solve(nu_init=2, **inp)
plotit([info1, info2, info3, info4],
['{0,2,1,2} (default)', '{0,0,1,2}', '{0,2,1,0}', '{2,1,2,1}'])
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 45.962 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 229 MB